Home > Textbooks > Selected Circuits > Power Supplies > Highly Reliable Voltage Supply >
Power Supplies
Highly Reliable Voltage Supply
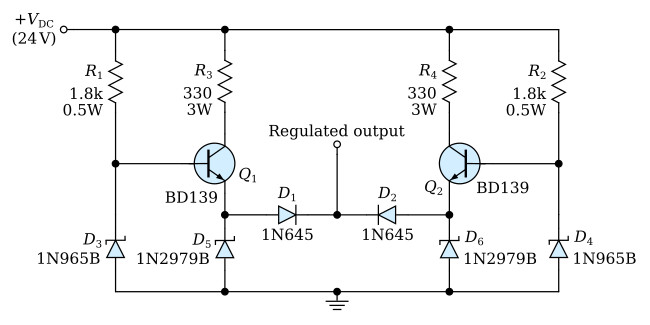
This is an example of a transistor regulated DC power supply circuit which features high reliability through redundancy. The circuit may be considered fail-safe because if any single component fails, or if one of many multiple component failures occur, the regulated output will remain the same with none of the other elements being overstressed electrically as a result of the failure.
Zener diodes, D3 and D4, provide the desired regulated voltage at the emitters of transistors, Q1 and Q2. Diodes, D1 and D2, provide isolation of the two sides so that the higher of the two voltages present at the emitters will appear at the output. Thus, if one side shorts or opens, the output is unaffected by the failure. Zener diodes D5 and D6 are included as additional protection should D3 or D4 fail. Resistors, R1 and R2, provide the required drive to Q1 and Q2. Resistors, R3 and R4, are used to reduce the dissipation at the collectors of Q1 and Q2.
The value of R1 and R2 can be calculated by considering the drive required by Q1 and Q2 to supply the total current required by the load. Each side should be capable of supplying this current, and the desired amount of bias current for D3 and D4.
The value of R3 and R4 can be calculated by considering the total current supplied by each transistor, the maximum allowable dissipation at the collectors, and the desired amount of bias current for D5 and D6.
Typical circuit elements and component values for 12V regulator are included in the figure.




